Hall Effect
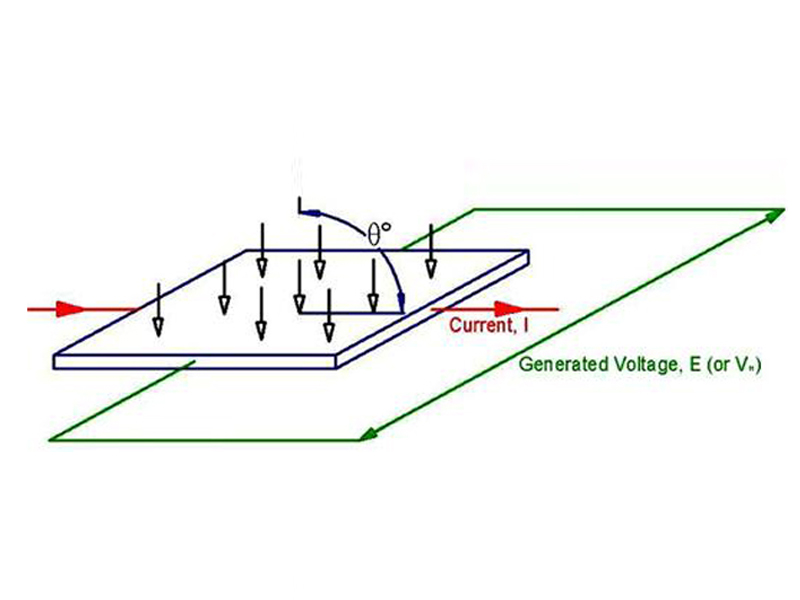
HALL EFFECT
A current I flows in one axis (typically 20· 200 mA).
A voltage E is created perpendicular to the current flow when a
magnetic field is applied perpendicular to the voltage and current planes.
The more perpendicular the applied field, the greater the voltage.
The Hall Voltage (VH) = E = BIL.sine(0°)
where:·
B = applied magnetic field
I = applied electric current
L = a constant for the Hall crystal material
sine = a trigonometric function, often appearing on calculators as “sin”
0° = angle between magnetic field and Active Hall device element